 The Story of Mankind Part II
The Story of Mankind
The Story of Mankind Part II
The Story of Mankind

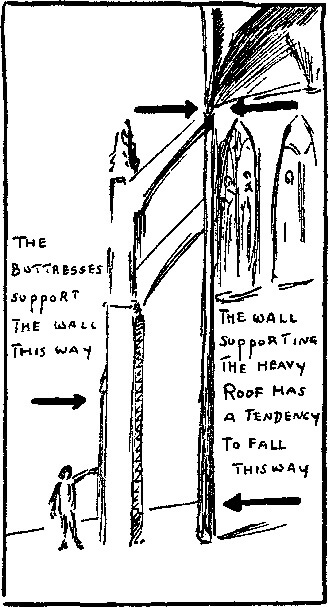
 The Story of Mankind Part II
The Story of Mankind
The Story of Mankind Part II
The Story of Mankind

Study the lesson for one week.
Over the week:
Activity 1: Narrate the Lesson
Activity 2: Study the Lesson Picture(s)
Activity 3: Complete Copywork, Narration, Dictation, and Coloring

Click the crayon above. Complete page 52 of 'World History Activities for Fourth Grade.'